AML and CFT Guide for Money Transfer Start-Ups
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT), are terms mainly used in the financial and legal industries to describe the legal controls that require financial institutions and other regulated entities to prevent, detect, and report money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
Every regulated entity should have appropriate AML as well as CFT checks and controls in line with the regulatory framework of the jurisdiction where the entity operates from.
To make it easier for Start-Ups, please find below the diagram of the AML/CFT Ecosystem:
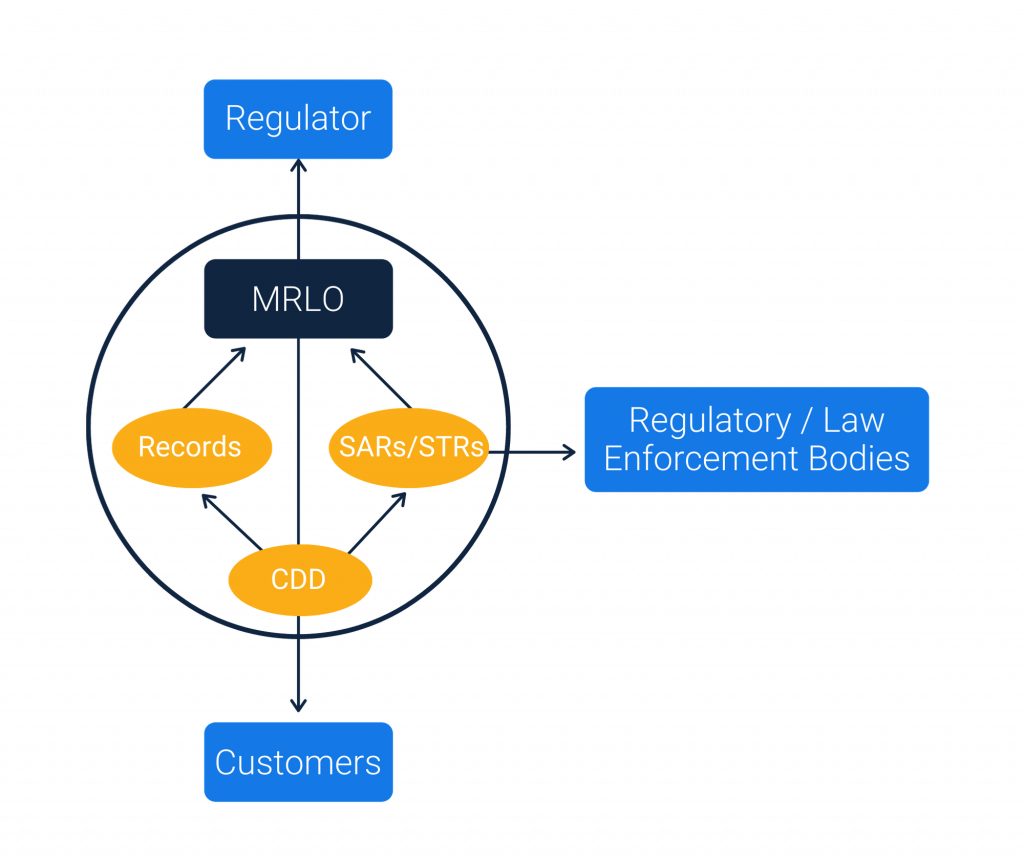
The ecosystem shown above shows the five core responsibilities of Money Transfer Start-Ups:
1. Onboard a Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO)
First and foremost, all start-ups must have a dedicated Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO) who is responsible for managing all compliance activities within the organisation. Depending upon the type and size of the business, there could be one or more members within the compliance team.
Aside from the MLRO, it is important that other stakeholders such as Directors, Senior Managers and even Shareholders familiarise themselves with the Payment Services and AML regulations within the jurisdiction where the business is registered.
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Each entity is responsible to identify the customers that they deal with. This step is known as the Know Your Customer (KYC). The MLRO has to identify the checks and controls that need to be in place to capture all the information needed from the customers as part of the KYC process.
Apart from KYC, the entity must also maintain the Customer Due Diligence which is mainly to do with checking the customers registering against the watch lists and the transaction patterns of the customers.
3. Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
The entity is required to conduct appropriate investigations whenever an event such as a transaction monitoring alert or a sanctions match occurs. The MLRO has to validate such investigations further and need to report to the local regulatory bodies in the form of Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) or Suspicious Transaction Reporting (STR).
4. Record Keeping
The entity is responsible to maintain records of all their customers and transactions for a minimum period of 5 years or as per the guidelines of the local regulatory bodies. The MLRO has to ensure that the data captured from customers for identification and transaction purposes are stored securely and accessible to the authorized individuals of the entity whenever needed. Apart from customers and transactions data, the entity should also maintain the records of all the SARs/STRs.
5. Registering and Reporting to Regulators
The entity is responsible to have the registration done with the relevant regulatory bodies in the jurisdiction where the entity operates from. The entity should also be aware of all the reporting obligations in order to submit reports related to the customers or transactions data to the relevant regulatory bodies in the jurisdiction.
Whether you are a start-up or an established Money Service Business, it is very important that the AML policies and procedures are clearly incorporated within your business model. For more information, advice and support, please contact us.
RemitONE provides proven compliance products for Money Service Businesses and Central Banks and would be delighted to help your business. Contact marketing@remitone.com or call +44 (0) 208 099 5795.
Video: Remittances in Africa – Market trends, regulation, challenges and opportunities
2020 was far from a banner year for many industries. But it is a year in which the remittance sector revealed itself to be defiantly resilient. The world bank projected a 20% fall in global remittance at the very start of the pandemic but by October they’d revised that figure to just a 7% drop, to be followed by another 7% drop this year (2021). This initially predicted fall was, by all accounts, supposed to have a particularly significant impact in Africa where migrant workers send around £11 billion per year.
RemitONE Associate Sales Director Oussama Kseibati feels that these are figures we always needed to take with a pinch of salt, not only because Africa is a region that is often underestimated on an economical level but because many countries there still lack the capability to capture data accurately. He adds: “Africa is also still a region where physical transfers are more common and it is harder to track physical transfers. That’s why these figures should be seen less as empirically accurate projections and more as rogue guidelines to give us a feel for how the market might be moving.”
To delve deeper into the current climate in Africa, Oussama recently hosted a webinar attended by four esteemed panellists with expert knowledge of the regional remittance landscape. Muhammad M. Jagana, CEO of Kuringo, Sidharth Gautam, Head of Sales at AZA Finance, Leon Issacs, CEO of DMA Global and Linus Adaba, Head of Group Remittance Distribution at Ecobank lent us their thoughts and feelings on the trends, regulations, challenges and opportunities facing Africa in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
To see the Q&A answers from our panellists click here.
Was 2020 as bad as expected?
If we’ve learned anything in the last 12 months, it’s that there’s always a risk in sticking your neck out for figures and projections. Nobody wants to die on that hill. In Africa, however, remittance continued to grow and thrive regardless of the pandemic and the World Bank’s scaremongering. Indeed, remittance was actually up by as much as 75% in the Gambia and 50% in Zimbabwe and even in developed countries such as Kenya, Morocco and Egypt, there were gains of around 12%.
Leon explains: “We’ve been hearing hundreds of positive stories of volumes from remittances across the region and we can only assume that’s because the migrants sending money home have a greater need to do so right now when we’re in the midst of a global crisis.”
Another key factor is the impact of the crisis on the informal market. Travel is particularly difficult right now and that means that many of the informal operators that were relying on physically moving cash just closed down after the pandemic forced travel to a standstill. The physical barriers put up between South Africa and Zimbabwe, for example, mean people were forced into using formal, regulated channels.
Leon adds: “Of course, there is also the major impact of digital to take into account, which makes it easier for people to transfer money and Africa has been dipping its toes into that particularly reservoir for a while now.”
How did Intra Africa remittances grow in 2020?
Linus feels that the remittance industry is a resilient one that tends to thrive in moments of crisis, so he’s not surprised it defied the World Bank projection. He explains: “Africans don’t forget home and they are very family-focused. That’s why I feel the African market grew so substantially in 2020. COVID provided a situation where, more than ever, people were willing to send money home.”
Where a partner has had a relationship with any other partner within the continent that allows transactions to happen between bank accounts or mobile wallets, that’s helped business for MTOs. More importantly, the government’s of most African countries saw remittances as COVID palliative. So they were quite willing to help facilitate these Intra African payments and even, in some cases, dedicated certain hours where people could queue and collect physical remittances while keeping safe and socially distanced.
Linus adds: “Some other countries like Kenya, for example, also increased the potential amount of each transaction per person. This not only meant less physical contact but it also meant that people were able to move more money more quickly between countries.” When you also factor in the various economic rules in place in various regions within Africa that allow for freedom of movement, it’s easy to see why Intra African remittances have been allowed to flourish.
As far as what needs to be done to boost the market, Leon adds: “To put it into context, the World Bank once estimated that for every $3 circulating within Africa, $2 originated within the continent. Most people look at Africa as one country rather than 55 and as somewhere that’s dependant on remittances from the rest of the world, but that’s not really the case.” He does believe, however, that there needs to be a regulatory shift in many countries to allow for easier transfer of money and this means allowing for different types of entities to operate alongside more traditional or formal channels.
How is technology going to help?
Currently, the cost of sending remittance to Africa is the highest rate in the world at around 9%. That’s around 5 times more costly than almost anywhere else and according to Oussama, the reason for this is simply because of the heavier reliance on cash payouts. Sidharth agrees, explaining: “For cash, you need so much more logistical support in terms of manpower, not to mention the actual physical locations. So technology is hopefully, in the long term, going to mean these costs reduce quite substantially, perhaps more in line with Southeast Asia where the rate is only around 2%.”
Leon believes that Africa is a hotbed for technology right now but that governments need to get involved on a deeper level to facilitate a safe space for transfers to happen between channels. This is something Mohammed also touches on, explaining that one of the problems is: “How many different currencies there are in Africa, which leads to issues with exchange rates.” He feels that a “single African currency” would be the most logical move. He adds: “We have 35 currencies in Africa and that’s always going to complicate remittances. The end user should not have to worry about exchange rates.”
This leads us quite neatly into the question of cryptocurrency. Sidharth has seen it being adopted in a big way through AZA’s separate crypto product, exploding from around $6,000 to $56,000 in just the last 2 quarters. He adds: “As regulations loosen up and mobile tech continues to build it will be more widely accepted as a means of payment, certainly within the next five years.”
Mohammed, meanwhile, feels adoption might be a little slower, mentioning that Nigeria recently stopped all crypto payments for B2B transactions. Leon, however, feels that it could become a big part of the solution in years to come but right now “people in Africa don’t have a good understanding of cryptocurrency yet.” That’s not to say they won’t in the future though and Oussama is hopeful that with time, that understanding will come. He believes that “a lot of end users right now are not using cryptocurrency as remittance but as more of an asset that will increase in value.” Education will undoubtedly play a major role in that regard.
How have the central bank measures promoting remittance impacted operations in Africa?
The regulation that the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) issued in December last year was designed to boost US dollar supply into the economy and simplify remittances by ensuring the beneficiary always collects the money in dollars. Linus explains: “70% to 80% of remittances to Nigeria in the last two years have been to bank accounts because of the instant delivery the banks offer.” So, the central bank changing the currency from Nigerian Naira to Dollar makes a lot of sense but Linus stresses it’s not necessarily a Nigerian “dollarisation.” What the central bank is doing, he argues, is simply allowing the individual to negotiate rates themselves and trying to unify the exchange rate because they “can see how remittances can be used to help aid development.”
Sidharth agrees though he says that AZA is always going to be a firm that promotes local currencies. He feels the regulation is going to provide a major challenge for the Naira even though he thinks it will be good for remittance and things will improve in the long term. Leon, meanwhile, explains that DMA is currently “working with the British government to try and understand the impact on the UK to Nigeria remittance corridor and how it has impacted both the senders and receivers.”
Right now he says it’s been a bit of a mixed bag, with some saying the measures have led to an increase in remittance and others saying it’s led to a decline and some of that’s due to the fact there was no notice given to some of the operators.
Oussama adds that it’s all part of a broad approach by CBN to try and manage the different exchange rates and the parallel market that exists in Nigeria where the exchange rate could be as much as 20% different to the official rate because the Naira isn’t floating. Over time there will almost certainly be tweaks made to the policy that will fit into the much broader range of initiatives but in the short term, the CBN are at least now very much in a dialogue with the operators. If this continues then hopefully it won’t go the way of Zimbabwe a few years ago, where they had to essentially dollarise the whole economy because of rampant inflation and overvalued local currency.
Resilience of Remittance
Generally speaking, the future looks bright for the African remittance sector as long as local governments and banks are willing to invest in regulatory change and incentivise a shift towards digital payments. There are definitely a few significant challenges to overcome in terms of financial inclusion and KYC but advancement in technology is a perfect solution and Africa is by no means on the back foot as far as technology is concerned.
To read more on what our panellists have to say regarding the more specific challenges facing mobile adoption in the region, click here for our companion piece or check out the full webinar here. If you are a money service business interested in expanding into the region, meanwhile, RemitONE is an award-winning provider of MSB technology.
If you need support with all your operational needs please contact us by emailing marketing@remitone.com to see how we can support you.
Panel Q&A
Q1. Can you provide an overview of the licensing regime in Africa? What licences do PSPs and Telcoms need to be able to conduct intra-Africa and international payments?
Muhammad: I believe this is one area that African governments can use to unleash huge opportunities to elevate disruptions in this domain which can help propel ‘The last Mile of the Financial Inclusion Journey’. The challenge in most African countries is that most GSM/Telcos are so flushed with cash (capital) compared to new FinTech companies that sometimes the offerings from these big operators are difficult to match.
Also, because of legacy infrastructures (Anglophone, Francophone, different currencies, FX regulations) it makes it impossible to effectively promote intra-African remittances, and scale to the potentials that are there. For example, Kuringo was in discussions with a potential partner in Ghana to explore the GM/GH corridor. We faced several bottlenecks, such as both our currencies (Dalasi/Cedi) are not convertible and we opted to use USD. Then our partners required waivers from the Central Bank of Ghana because in order to settle us in the US they have to fulfil FX control restrictions. In the end we abandoned the project because of complicated regulatory issues.
Q2. How do the panellists evaluate intra-Africa transactions vis-a-vis AcFTA which was launched in January 2021?
Linus: It is a good initiative that is more than overdue. It will facilitate big ticket payments of goods and services. Major countries in Africa have executed the treaty which shows political will to make it a success.
Muhammad: Huge potential if only there could be a single digital currency that could be used to settle intra-Africa trade, hence mitigating exchange losses. With over 35 currencies used across Africa, SME who are the backbones of most economies would be able to fully benefit from AcFTA.
Q3. With regards to AML/CFT and remittances, is Africa a significant corridor and has the pandemic accelerated this; what new typologies have emerged in this past year?
Linus: Regarding AML/CFT Africa is certainly a significant corridor. AML/CFT has always been a concern for regulators which each remittance scheme is expected to put in place before the advent of Covid-19.
Q4. Have you seen an increase in remittance/FinTech partnerships since 2020 and is Ecobank looking at new ways to partner international players to increase value added services into Africa?
Linus: Yes certainly.
Q5. Do you believe central banks are likely to open up in the ways others have regarding Cryptocurrency? E.g. CBDCs?
Leon: Over time they will, but it’s unlikely to be in the near future.
Sidharth: Medium to long term, Crypto will gain momentum in Africa due to the high cost of sending remittances and over-relying on cash in the continent. But this has its own challenges like central banks, regulations and onramp/offramp from local currencies.
Q6. Inoperability is a big issue with Telcos in Africa, to boost remittances even within the same country. Is it a regulatory, technology or lack of will issue?
Linus: Interoperability required a clearing house to succeed. Some aggregators can offer this service, but there is need for a clearing framework within the region or country by the regulator to make this effective. Telcos are beginning to find ways on how to cooperate in this respect, but candidly the services on an impartial arbiter are required.
Leon: Completely agree. Most Telcos don’t want to cooperate, similiar to how MTOs were 15 years ago. Regulators need to get involved to make it happen.
Sidharth: Except Nigeria, where there is some sort of interoperability/common rails due to Interswitch, this is still a distant task and much is needed to make this happen. CBs/regulators have to play a pivotal role in making this happen both for bringing down the cost and making remittances happen real-time across the continent.
Q7. What are your views on Telcos doing some banking functions, given that Telcos have huge subscribers etc? Are banks not concerned about this for the future, as they appear to be doing banking work and revenues may dwindle for banks?
Linus: Telcos are assisting to expand financial includion and deploring affordable technologies or infrastructures where the banks cannot venture becayse of a typical bank operating model. I see collaboration between Telcos and banks rather than competition. Each part has assets to offer in the financial inclusion narrative.
Leon: Exactly right. Telcos will be the distribution channel and banks the service provider – these will be white-label product providers.
Q8. Do you think the new regulations in Nigeria are against African money transfer companies who are sendig from Africa to Nigeria?
Linus: No
Leon: It is not against African MTOs, indeed, it should be helpful to them.
Q9. Regarding one of Leon’s explanations of regulatory frameworks being challenging for intra-African remittances, how does this work with Crypto where there is no regulatory framework in place?
Leon: Great question. Unfortunately, because there is no framework there is no approval to operate these services. The only way around this is to obtain a letter of consent or to use sandboxes. It will take time but is not high priority at the moment for most central banks.
Q10. Do you think that Cryptocurrencies can be a solution to solve settlement problems for intra-Africa cross-border remittances?
Leon: They can help will illiquid currencies or imperfect settlement processes. But they are not an answer for consumers right now unless there are ways for people to exchange Crypto for local currency.
Q11. Will the change to USD in Nigeria have much impact especially slowing the black market traders? And what is the impact of this Naira to USD change?
Linus: There will be impact. More awareness on the current changes in remittance payout in Nigeria may change this. The beneficiary of the remittance is involved in the Naira value for the Dollar received which is determined by market forces rather than policy fiat.
Q12. Why do African Money Transfer players not want to play outside of Africa and directly service the African diaspora?
Linus: RapidTransfer, for example, is in Europe serving African diaspora. The success of this new addition to the 33 countries where Ecobank is operating in Africa could spur future expansion to other countries where we have diaspora presence.
Q13. Nigeria was implementing two exchange rates concurrently. What are the benefits and challenges of this policy? How can Ethiopia learn from stringent rules and regulations like this?
Linus: Yes, before the switch to USD payout by policy of November 30th 2020, the second official exchange rate is a premium above the first for Naira payout for inbound remittances into Nigeria. It was to reward the Nigeria diaspora to channel their hard-earned money back into the country and to use approved schemes and instruments. Central banks do share experiences, I would advise that tour central bank gets in touch with the Nigerian central bank to compare notes.
Q14. When and where can we obtain Leon’s consumer research?
Leon: Not sure of the exact timing, but we expect this to be around the end of April or early May. We’ll be happy to circulate it.
Q15. Do you think that remittance in our region is at the point that you expected it would be 5 years ago?
Leon: I think it is progressing faster than I would have expected.
Muhammad: The evolution of affordable smart phones and mobiles in general, we have seen a huge growth in the remittances both in the formal an informal market. Today most informal operators (within countries) are using WhatsApp, text message and mobile phone calls to move money within border and across/intra-Africa.
Q16. Regarding the bound on Crypto in Nigeria and the fat that people have to collect USD in place of Naira, what is the advice for a startup?
Linus: Play to the rules and seek partners and banks that share your business vision.
Q17. What are your views on the introduction of individual CBDCs and its effect on intra-Africa remittances and global remittances; what harmonisation is needed to move past the current status quo in terms of exchange rates?
Leon: A good but complex question. They can only be effective if there is much more digitisation in everyday payments in Africa. Ideally an intraregional currency would bring more stability.
Q18. What can be done to help the end users use their money in digital ways, but also have access to cash with more ATM machines?
Muhammad: The Last Mile Solutions for Africa might not be ATMs, but rather small corner/community shops that are dotted all over villages, towns, cities across Africa. How can we onboard them to accept digital payments and give them access to smart POS that would work on mobiles that can be used as withdrawal points (ATM, Payment Centres).
Leon: There needs to be much more digitisation in general life in African countries. This has to happen way before we worry about international payments. Remittances are relevant for payouts but only ride on domestic rails for this.
If you need support with any operational needs, or have further questions, please contact us by emailing marketing@remitone.com to see how we can support you.
Brexit is a done deal, but what does that mean for the remittance sector?
To say 2020 was a challenging year would be something of an understatement. If the pandemic wasn’t enough, we were then thrown headfirst into a Brexit deal that potentially threatens all UK businesses which trade with the continent. We’re on the other side of a very long, complicated and messy divorce but there are still so many things to unpack and digest, particularly as far as the financial sector is concerned.
Back in 2016, when the referendum result was first announced it was a shell shock to the money transfer and wider financial services industries. But that was almost five years ago now and while London certainly doesn’t look set to be dethroned as a world business capital any time soon, there has certainly been a minor exodus as the UK becomes more of an isolated island.
The immediate ramifications of Brexit
Before the ink could dry on the referendum result, money service businesses across the country began to prepare their backup plans. Of course, those that only served customers in the UK would remain unaffected, as would those operating as SPIs. But those operating under the category of APIs that had a large customer base or agent network in the continent had to apply for new MSB licenses from scratch.
Back in 2017, we posited that it would be the change in banking passporting that would have the most significant impact on money transfer and the wider financial services market. Passporting rights in the years before Brexit helped UK businesses to expand into EU states quickly and at minimal cost and post-Brexit, those privileges would be all but expunged.
Making sense of the Brexit fallout
The immediate fallout of the 31st of December was, as was predicted, that MTOs lost passporting rights. This had a major knock-on effect, with all the MTOs that had accounts within Europe and were safeguarding their funds. A month or so later, we’re now seeing those accounts either being closed or laboured with exorbitantly hiked-up SEPA payment fees.
The UK is also going to find itself fighting for itself as far as regulations are concerned. The European payment regulator that oversees the SEPA payment network will have no interest in fighting for a country that essentially tossed it to one side, after all.
The vast majority of UK-based MTOs will undoubtedly have lost European clients over the last 12 months and most European MTOs will have lost many UK-based clients too. Indeed, all MTOs that rely primarily on inter-European banking will probably lose many more in the ensuing months.
The impact has been compounded by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent global lockdowns. One thing this has done, however, is catalyse a deeper digital penetration in the money transfer sector, with estimates that the digital hold on the sector grew from 20% to 30% from 2019 to 2020. That means remittance software and fintechs are going to play a larger role going forward. But that’s not necessarily a bad thing and it might not be the only silver lining.
Is there a plus side for remittance?
While it might have moved on from the EU from a regulatory perspective, the UK is still an important part of the payments network and London will remain well-positioned for money transfers. Indeed, for MTOs with a higher volume of foreign exchange transfers, London is still arguably the best place to do the business thanks to its abundance of high net-worth individuals and the number of major international businesses that call it their home.
We’ve also seen many companies abandon the UK for greener pastures and some European countries (such as Spain and The Netherlands) have greeted these companies with open arms. Other companies, particularly smaller ones, have turned to mergers or partnerships with larger competitors to be able to access their European clients.
Thankfully, as the UK was wise enough to adopt the PSD2 open banking regulations back in 2018, the businesses that could afford to expand into other EU states could do so without being tangled up in miles of expensive bureaucratic red tape. But it’s still an expense that many smaller MTOs could have done without.
Then there are those who have proselytised the idea of pivoting away from Europe entirely. Michael Kent, the Cofounder of Azimo, for example, believes we should be looking towards Africa, where remittance is proving to be a crucial lifeline in the absence of governmental pandemic support.
According to RemitONE CEO Anwar H Saleem, however, there is no need for MTOs to panic as long as they can learn to adapt and lean into the changes. He explains: “London has always been a major financial hub for Europe and this is not going to change any time soon now that we’re no longer a member of the EU. It will, however, push those businesses that remain in London to innovate and lead the way. RemitONE are already committed to charting this new course with confidence.”
Can UK money transfer businesses survive Brexit?
While it didn’t end up being the highly prophesied ‘no-deal Brexit’ for most, for the financial services and remittance sector, it might as well have been. With no agreement on the regulatory equivalence between the EU and the UK, there is still a lot of work to be done.
For those operating in both the UK and the EU, there are certainly some tough choices to be made. But ultimately, it’s going to be up to the UK and the MTOs that have chosen to stay behind to ensure it remains relevant and doesn’t lose its standing on the global remittance stage. Whatever the next few years have in store for us, the best thing any MTO can do is arm themselves with the facts and prepare for every and any eventuality.
If you’re uncertain about the future and are looking for support regarding licensing issues post-Brexit, RemitONE is ready to take your call. Using our industry-leading bespoke and secure money transfer software, we can help any established firm or new entity looking to establish in the UK or Europe to navigate the increasingly complicated logistical and regulatory waters spun up by Brexit.
For more information or to speak to one of our experts please email marketing@remitone.com